Structural Organisation of a Cell
Structural Organisation of a Cell: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Osmosis, Nucleus of a Cell, Prokaryotic Cell, Eukaryotic Cell, Cytoplasm, Cell Organelles, Cell Wall, Cellulose, Endoplasmic Reticulum, Golgi Apparatus, Lysosomes, Mitochondria, Plastids, Chloroplasts, etc.
Important Questions on Structural Organisation of a Cell
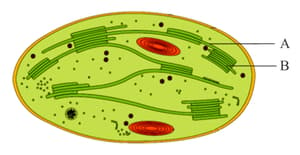
Identify A and B in the given figure and select the correct option.
Assertion: Lysosomes are often called as 'suicidal bags' of a cell.
Reason: Lysosomes contain hydrolytic enzymes capable of digesting cellular waste.
Match column I with column II and select the correct option from the codes given below.
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum | (i) Amoeba |
| B. Lysosome | (ii) Nucleus |
| C. Nucleoid | (iii) Bacteria |
| D. Food vacuoles | (iv) Detoxification |
| E. Chromatin material and nucleolus | (v) Suicidal bag |
What do you understand by the term ATP?
Name the organelle that is called the power house of the cell.
Define nuclear membrane.
The genetic material in prokaryotes is termed nucleoid and not nucleus. Why?
Deplasmolysis causes shrinkage of a plant cell.
Define the term deplasmolysis.
The cell organelles that do not have a plasma membrane or any kind of membrane are called _____ cell organelles
Write two differences between membranous and non-membranous cell organelles.
Non-membranous organelles are surrounded by a plasma membrane.
Describe few characteristics of non-membranous cell organelles.
Golgi complex is a membranous cell organelle.
Mitochondria is a _____ membrane cell organelle.
Write the two features of membranous cell organelles.
Nucleus is the non-membranous cell organelle.
What do you understand by membranous cell organelles?
Cell membrane is a made up of
Write the differences between plant cell and animal cell.
